The key differences and their roles in Microsoft Fabric
In the world of modern data architectures, terms such as data warehouse, data lake and lakehouse have become firmly established. However, many customers find it difficult to differentiate between these terms, especially when it comes to Microsoft's new comprehensive analytics platform, Microsoft Fabric. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at these three key concepts, discuss their respective advantages and disadvantages, and discuss how they can be used within Microsoft Fabric.
About the author

Alexander Jungmann
Data Engineer
About the author

Alexander Jungmann
Data Engineer
The key differences and their role in Microsoft Fabric
In the world of modern data architectures, terms such as data warehouse, data lake and lakehouse have become firmly established. However, many customers find it difficult to differentiate between these terms, especially when it comes to Microsoft's new comprehensive analytics platform, Microsoft Fabric. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at these three key concepts, discuss their respective advantages and disadvantages, and discuss how they can be used within Microsoft Fabric.
Microsoft Fabric: A brief overview
Microsoft Fabric is a platform for the development and management of distributed systems that emphasises scalability, reliability and efficiency. It enables developers to create complex, highly available and scalable applications that can be distributed across multiple data centres. If you would like to learn more about Microsoft Fabric, you can find our detailed blog article here:
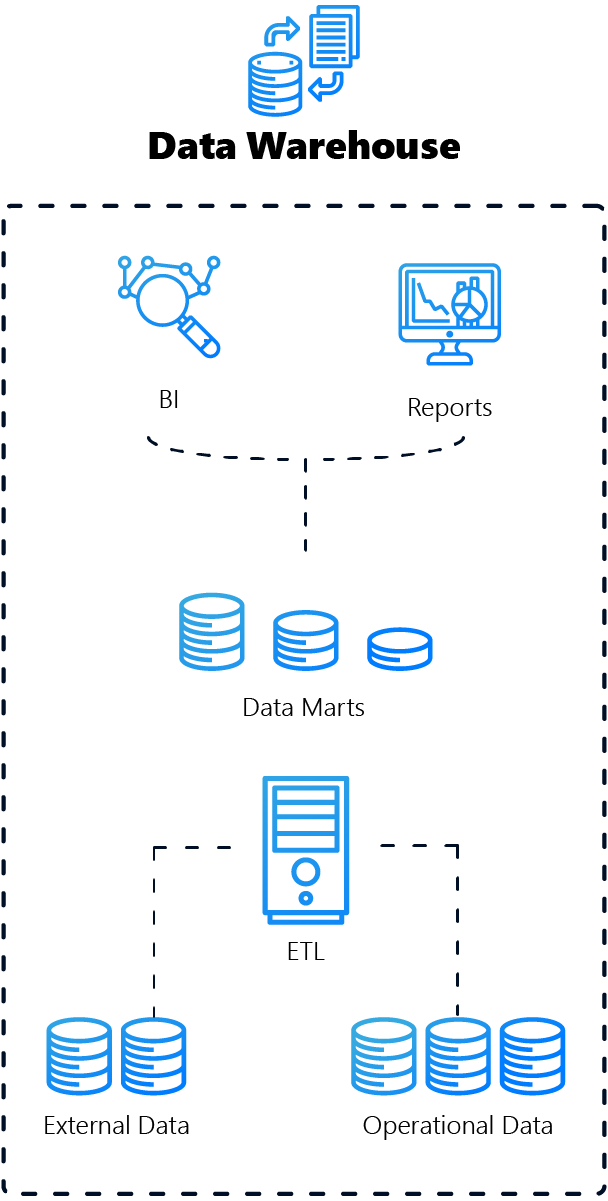
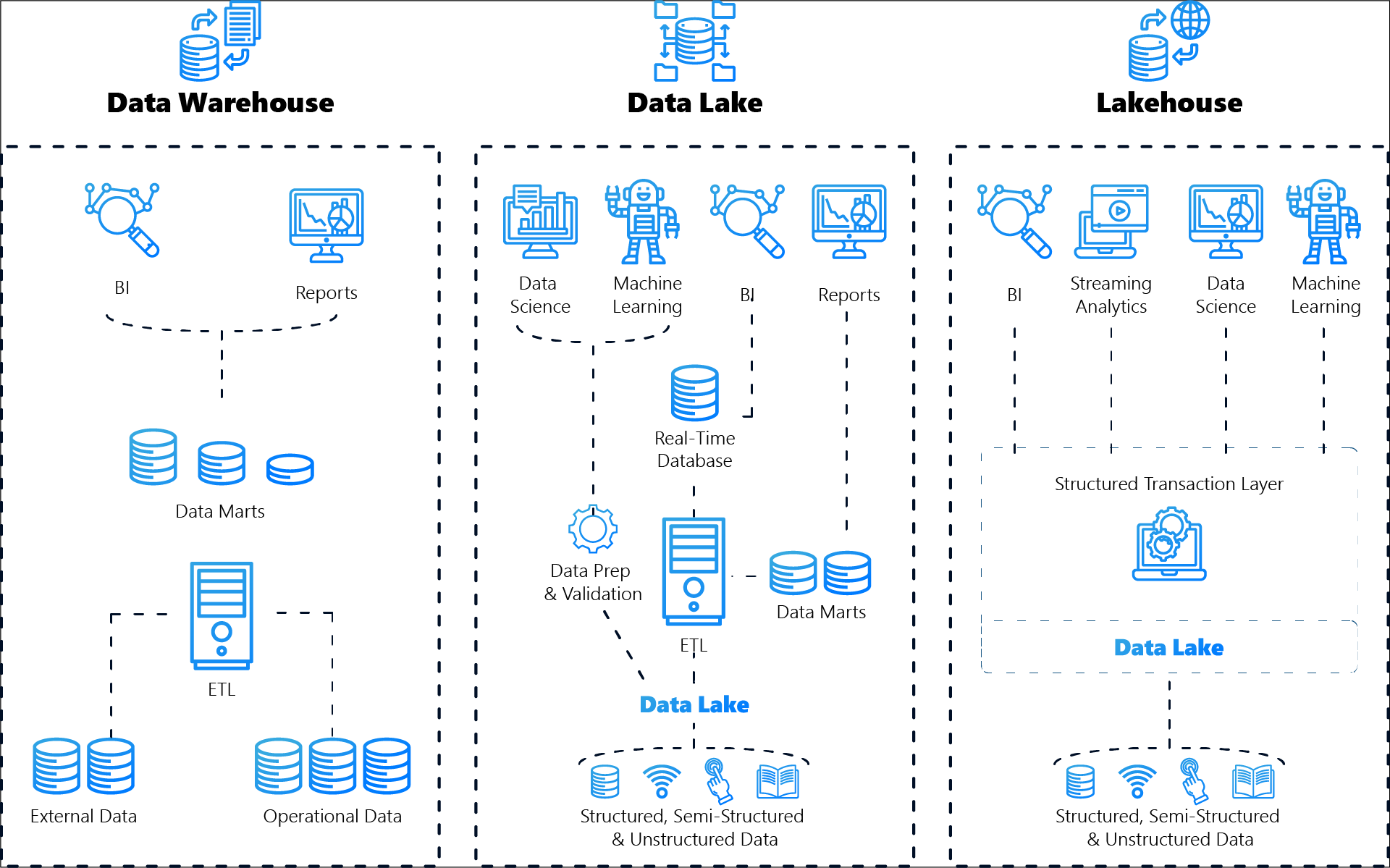
1. data warehouse: the structured analyst
A data warehouse is a database environment that is optimised for the storage and analysis of structured data. It is ideal for companies that want to efficiently process and analyse large volumes of organised data.
Advantages
High performance for queries
The predefined structure means that queries can be carried out quickly and efficiently.
Consistency and quality
The ETL process (extraction, transformation, loading) cleanses the data and keeps it consistent.
User friendliness
Optimised for business intelligence (BI) and reporting.
Disadvantages
Less flexibility:
Mainly suitable for structured data.
Time-consuming pre-processing process
ETL can be time-consuming, especially with large volumes of data.
The role of Data Warehouse in conjunction with Microsoft Fabric

Integration with fabric tools
Microsoft Fabric can facilitate the integration of data warehouses with other Microsoft tools such as Azure and Power BI, resulting in improved data analysis and reporting.
Improved performance and scalability
With Microsoft Fabric, a data warehouse can benefit from automated scaling and resource optimisation, which is particularly important for large volumes of data and complex queries.

Enhanced security and compliance
Microsoft Fabric can provide robust security and compliance features that are essential for data warehouses in regulated industries.
1. data warehouse: the structured analyst
A data warehouse is a database environment that is optimised for the storage and analysis of structured data. It is ideal for companies that want to efficiently process and analyse large volumes of organised data.
Advantages
High performance for queries
The predefined structure means that queries can be carried out quickly and efficiently.
Consistency and quality
The ETL process (extraction, transformation, loading) cleanses the data and keeps it consistent.
User friendliness
Optimised for business intelligence (BI) and reporting.
Disadvantages
Less flexibility:
Mainly suitable for structured data.
Time-consuming pre-processing process
ETL can be time-consuming, especially with large volumes of data.
The role of Data Warehouse in conjunction with Microsoft Fabric

Integration with fabric tools
Microsoft Fabric can facilitate the integration of data warehouses with other Microsoft tools such as Azure and Power BI, resulting in improved data analysis and reporting.

Improved performance and scalability
With Microsoft Fabric, a data warehouse can benefit from automated scaling and resource optimisation, which is particularly important for large volumes of data and complex queries.

Enhanced security and compliance
Microsoft Fabric can provide robust security and compliance features that are essential for data warehouses in regulated industries.
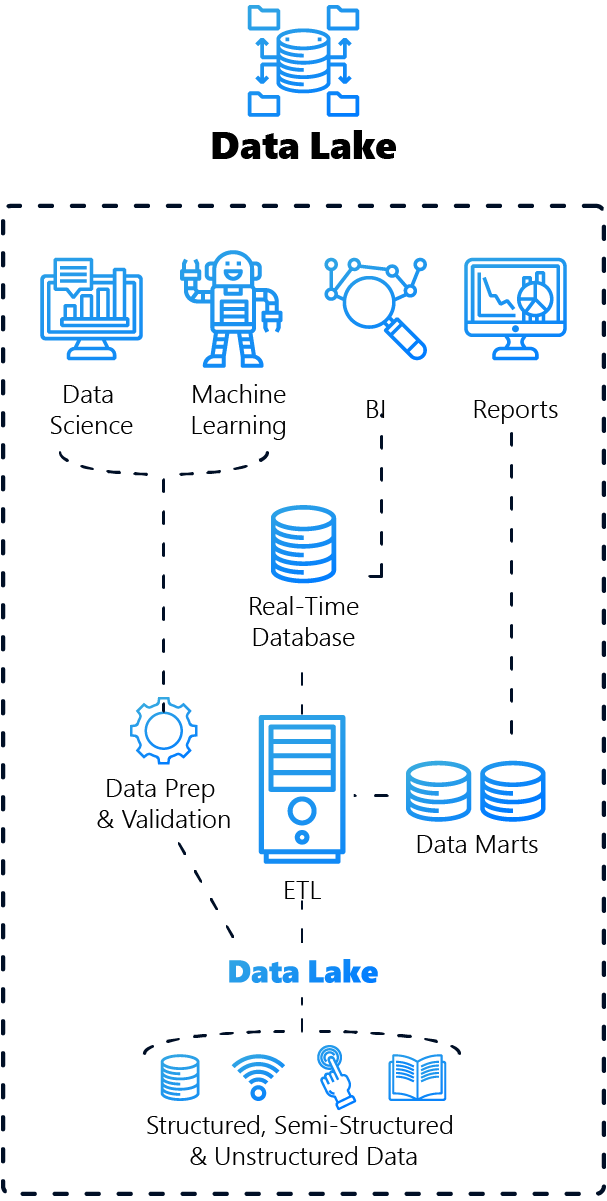
2. data lake: the versatile data store
A data lake is a storage system that stores large amounts of raw data in its native format. This can be structured, semi-structured or unstructured data.
Advantages
Versatility
Can store a wide range of data types.
Flexibility
Schema-on-Read enables flexible data analysis.
Scalability
Suitable for very large amounts of data.
Disadvantages
Complexity
Can become confusing without appropriate management.
Challenges in data quality
Quality assurance is more complicated because the data is stored in raw form.
The role of Data Lake in conjunction with Microsoft Fabric
Seamless data integration
Fabric makes it possible to aggregate and manage data from different sources and formats in one data lake, which increases the flexibility and efficiency of data utilisation.

Advanced analytics capabilities
Integration with Microsoft Fabric makes it easier for advanced analytics tools and AI services to access the data stored in the data lake, improving insight extraction and decision-making.
Optimised data management
Microsoft Fabric can help overcome the challenges of data management in a data lake by providing tools to better organise, secure and monitor data.
2. data lake: the versatile data store
A data lake is a storage system that stores large amounts of raw data in its native format. This can be structured, semi-structured or unstructured data.
Advantages
Versatility
Can store a wide range of data types.
Flexibility
Schema-on-Read enables flexible data analysis.
Scalability
Suitable for very large amounts of data.
Disadvantages
Complexity
Can become confusing without appropriate management.
Challenges in data quality
Quality assurance is more complicated because the data is stored in raw form.
The role of Data Lake in conjunction with Microsoft Fabric

Seamless data integration
Fabric makes it possible to aggregate and manage data from different sources and formats in one data lake, which increases the flexibility and efficiency of data utilisation.

Advanced analytics capabilities
Integration with Microsoft Fabric makes it easier for advanced analytics tools and AI services to access the data stored in the data lake, improving insight extraction and decision-making.

Optimised data management
Microsoft Fabric can help overcome the challenges of data management in a data lake by providing tools to better organise, secure and monitor data.
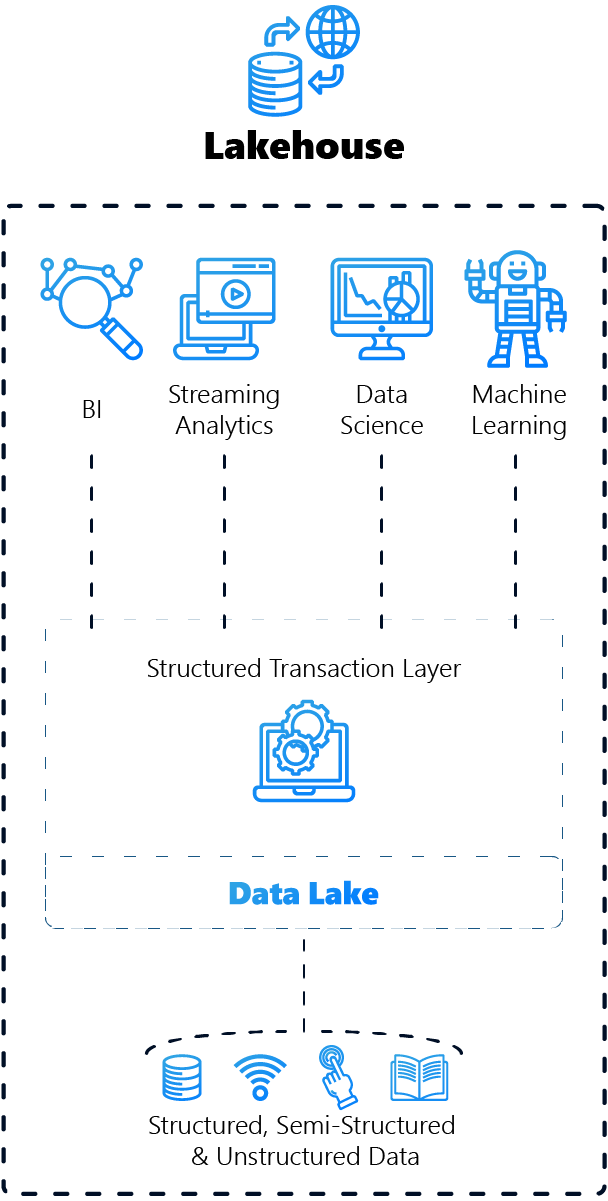
3rd Lakehouse: The best of both worlds
The lakehouse model combines the functions of a data warehouse and a data lake by uniting the structure and efficiency of a warehouse with the flexibility and scalability of a lake.
Advantages
Flexibility and structure
Supports both structured and unstructured data efficiently.
Data quality
Ensures high standards of data quality and reliability.
Support for BI and machine learning
Provides a standardised platform for various analysis needs.
Disadvantages
Complexity in the implementation
Can be demanding to set up and manage.
Costs
Potentially higher costs by combining both systems.
The role of Lakehouse in conjunction with Microsoft Fabric

Standardisation of data architectures
The lakehouse model can be optimally utilised by Microsoft Fabric by combining the structured analysis capabilities of a data warehouse with the flexibility of a data lake.

Support for real-time analyses
With Fabric, a lakehouse can react to data changes in real time, which is important for time-critical applications such as financial analyses or e-commerce.

Promoting collaboration and accessibility
Microsoft Fabric can facilitate access and collaboration between different teams and departments by providing a single, accessible platform for all data requirements.
3rd Lakehouse: The best of both worlds
The lakehouse model combines the functions of a data warehouse and a data lake by uniting the structure and efficiency of a warehouse with the flexibility and scalability of a lake.
Advantages
Flexibility and structure
Supports both structured and unstructured data efficiently.
Data quality
Ensures high standards of data quality and reliability.
Support for BI and machine learning
Provides a standardised platform for various analysis needs.
Disadvantages
Complexity in the implementation
Can be demanding to set up and manage.
Costs
Potentially higher costs by combining both systems.
The role of Lakehouse in conjunction with Microsoft Fabric

Standardisation of data architectures
The lakehouse model can be optimally utilised by Microsoft Fabric by combining the structured analysis capabilities of a data warehouse with the flexibility of a data lake.

Support for real-time analyses
With Fabric, a lakehouse can react to data changes in real time, which is important for time-critical applications such as financial analyses or e-commerce.

Promoting collaboration and accessibility
Microsoft Fabric can facilitate access and collaboration between different teams and departments by providing a single, accessible platform for all data requirements.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of modern data architecture, Microsoft Fabric proves to be a versatile ally. Whether you are working with structured, unstructured or a mixture of data types, understanding these key concepts is essential.
Do you have any questions?
Interested in exploring how Microsoft Fabric can revolutionise your data strategy? Let's dive deeper into the world of advanced data solutions together.